
Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Associate editor Steven Otte needed several wood water tanks for his layout, so he decided to scratchbuild them using stripwood and common materials. In part one of this two-part video, Steve shows you how he built the tank and the roof. […]
Read More…
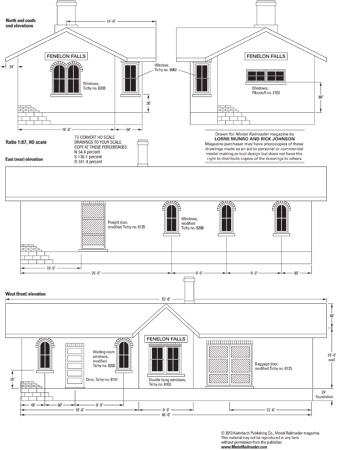
During a family vacation several years ago, I photographed the former Canadian National Ry. Fenelon Falls, Ont., station. This building stands on a now abandoned 55-mile-long rural branch line that once connected the town of Lindsay to Haliburton. The station houses an art gallery and now has board-and-batten sheathing. However, I’ve found several old pictures […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Sometimes you need to replace a turnout or other trackwork on your model railroad. In this video Cody Grivno shares his technique for replacing turnouts on Model Railroader’s HO scale MR&T layout, walking you through the project from cutting out the old rails […]
Read More…

Pelle Søeborg shows how he scratchbuilt a liquid-asphalt transfer terminal in the June 2013 Model Railroader. Back in the February 1994, Clyde Maybee Jr. showed how he modeled the industry on his layout. Click on the link to download a PDF of the original article. […]
Read More…
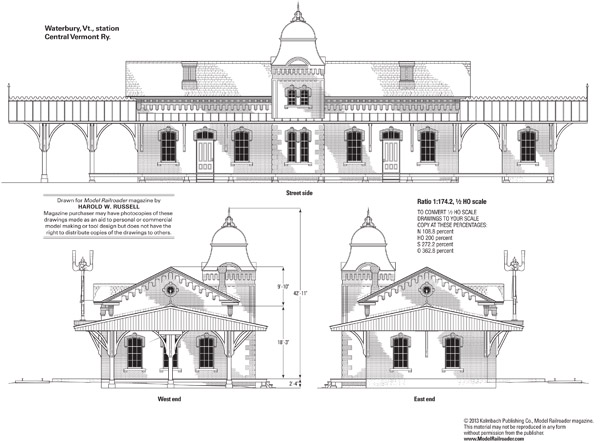
Waterbury, Vermont’s historic railroad station was built by the Central Vermont Ry. in 1875. The station was the centerpiece of Waterbury Village for more than 75 years, serving as the gateway to nearby attractions. Its main entrance faced the village green. Through the 1950s, it was the destination for the Central Vermont’s Ski Train, which […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page In this installment of Video Step by Step, Cody Grivno shows you how to build a low-relief structure kit that fits between the tracks and the backdrop. In part 2 he covers final assembly, weathering, and installation. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Our Winter Hill project railroad needed a lot of rock hoppers, and Cody Grivno shows you how he restenciled and weathered various Walthers models to fill out the fleet on the HO scale MR&T. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page In this installment of Video Step by Step, Cody Grivno shows you how to build a low-relief structure kit that fits between the tracks and the backdrop. In part 1 he covers assembling plastic kits and basic painting. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Water, rocks, trees, and more, this installment of Video Step by Step has it all. In part 2, Cody builds the riverbed and then pours the resin for the water. He also includes tips for making realistic ripples on the water’s surface. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Water, rocks, trees, and more, this installment of Video Step by Step has it all. In part 1, Cody shows you how he renovated an existing scene on the MR&T with new ground cover, trees, and freshly painted rocks. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Video Step by Step takes you start to finish through a modeling project. In this installment, associate editor Cody Grivno shows you how to build easy tree-covered hills to fit between the tracks and your backdrop. […]
Read More…

Louisville & Nashville freight 864 from Norton, Va., to Corbin, Ky., meets Southern First 88, a coal turn from Andover to Yuma, Va., on the wye at Appalachia on May 23, 1969. Although wyes are commonplace on prototype railroads, they can be challenging to model. Ron Flanary A “wye” describes an area where three turnouts […]
Read More…












