
Canadian Pacific and Kansas City Southern have scheduled special stockholder meetings for votes on their proposed merger. Both meetings will be conducted online. CP will go first, on Dec. 8 at 11 a.m. EST, for shareholders to vote on the issuance of CP common shares for KCS stockholders. All shareholders of CP common stock as […]
Read More…
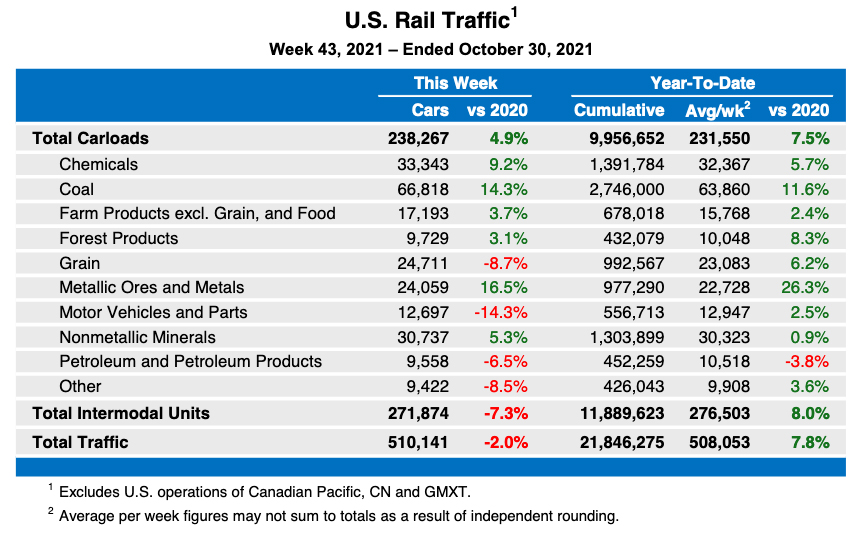
WASHINGTON — Intermodal issues continued to weigh on U.S. rail volume in October, as a 7.9% drop in intermodal traffic led to an overall decline of 2.8%, according to the latest figures from the Association of American Railroads. The overall drop came despite a 3.8% increase in carload volume. “For railroads, the supply chain challenges […]
Read More…
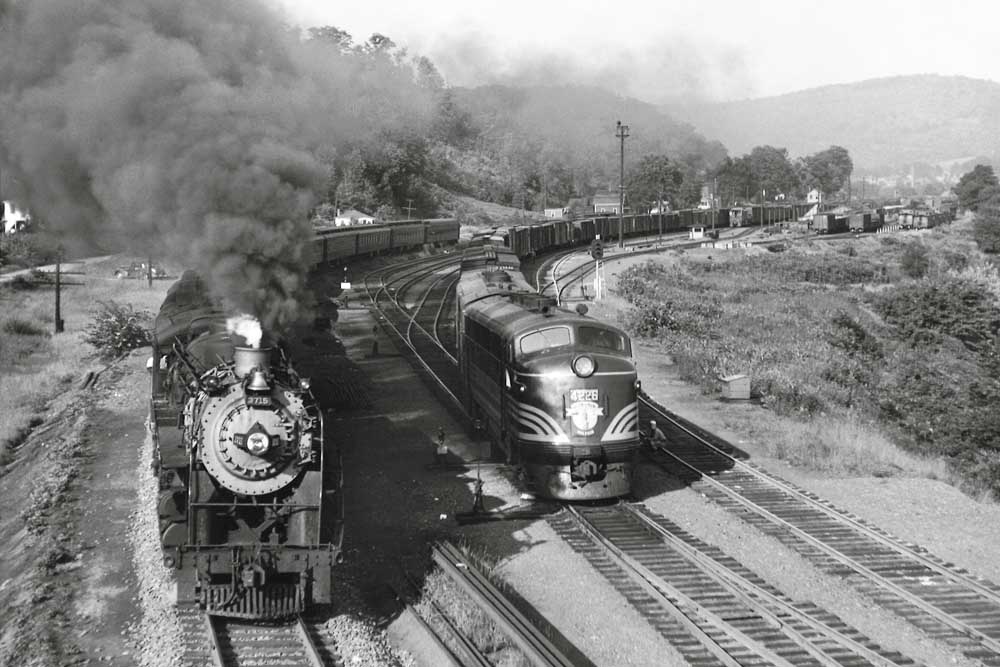

White River Junction A steam-powered, heavyweight passenger train passes freight JS4 departing the Boston & Maine’s White River Junction, Vt., yard with an A-B set of F units in 1947. Philip R. Hastings photo […]
Read More…

We took Lionel’s new legacy GP30 in Chicago & North Western livery out for a spin on our City Transfer & Terminal RR. It runs just as good as it looks! For a full review, check out the December 2021 issue of Classic Toy trains or click here. It also makes an appearance on Bob’s […]
Read More…

We took Lionel’s new legacy GP30 in Chicago & North Western livery out for a spin on our City Transfer & Terminal RR. It runs just as good as it looks! For a full review, check out the December 2021 issue of Classic Toy trains or click here. It also makes an appearance on Bob’s […]
Read More…

WASHINGTON — The Surface Transportation Board will allow a Minnesota company to proceed with its complaint against Union Pacific that alleges service reductions by the railroad violate UP’s common carrier obligation and constitute unreasonable practices. In a decision issued Tuesday, the board granted a request by Sanimax USA to partially revoke commodity exemptions and allow […]
Read More…
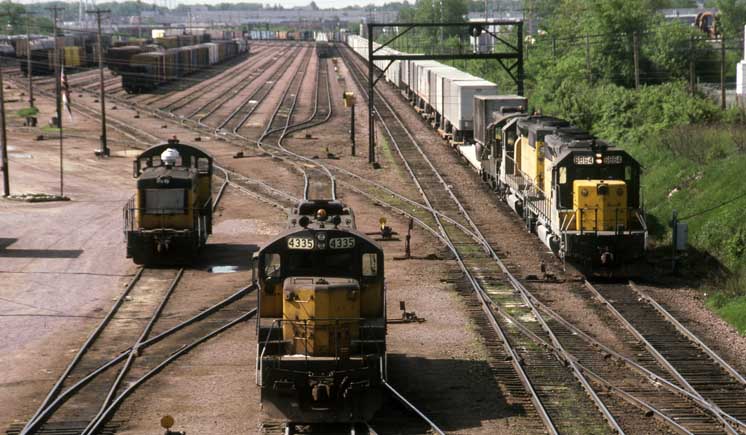

Train 477 Train 477 out of Chicago holds the westward main track at Butler, Chicago & North Western’s principal Milwaukee-area yard and site of the Wisconsin Division headquarters, in spring 1984. Chris Burger photo […]
Read More…

WASHINGTON — The Surface Transportation Board has laid out a 245-day schedule for submission of evidence and arguments on the merger application for Canadian Pacific and Kansas City Southern under a proposal released Tuesday afternoon — envisioning a longer process than the railroads had hoped for. The 245-day plan would proceed from last Friday, Oct. […]
Read More…
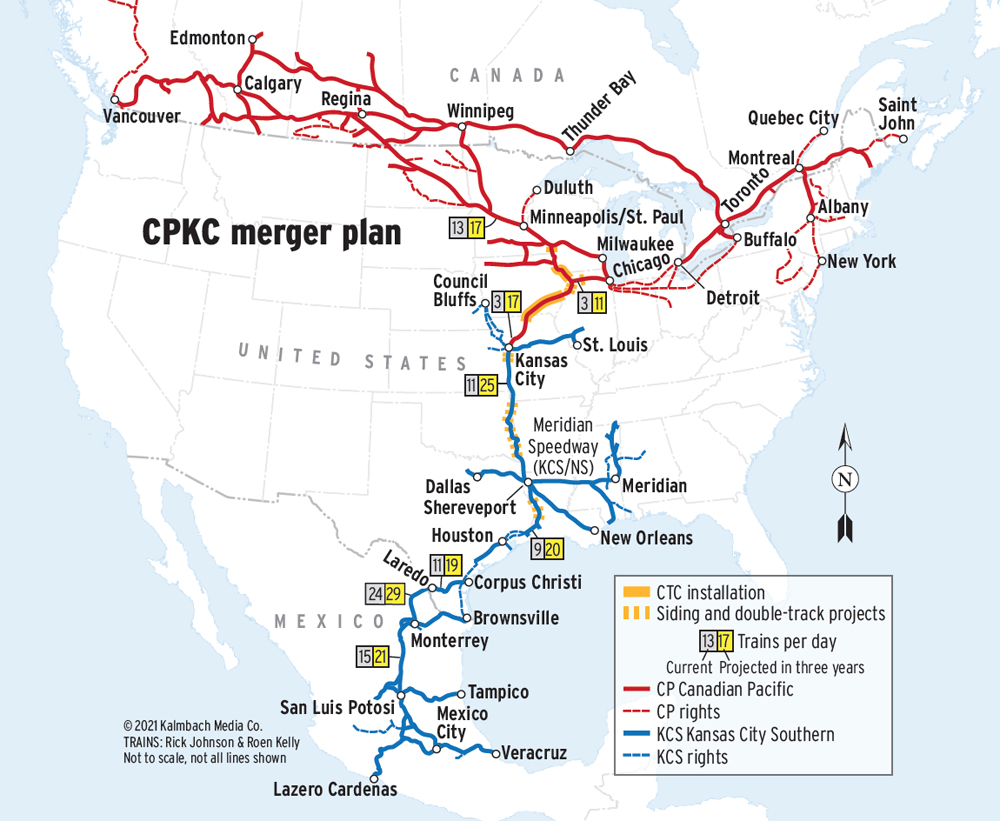
WASHINGTON – Canadian Pacific and Kansas City Southern say their proposed merger will generate significant traffic growth, with daily train counts on the combined system’s north-south spine projected to more than double within three years. The traffic details were among those included in the railways’ 4,342-page, 1-gigabyte merger application filed with U.S. regulators late Friday. […]
Read More…

My father was a closet railfan. He didn’t hang around the tracks or take pictures of trains. On the other hand, he was always more than happy to take us kids to almost any railroad yard or station if we asked. And he never told us to stay away from the tracks, perhaps swayed by […]
Read More…

MONTREAL — Canadian National has issued a seven-page document regarding the proxy fight led by activist investor TCI Fund Management in which it says TCI’s “motives are highly suspect and its approach to railroading is outdated, myopic, and destructive to longer-term value.” The “Letter to Stockholders” issued Tuesday morning by the CN board of directors […]
Read More…

CALTZONTZIN, Mexico — The latest blockade of Kansas City Southern de Mexico tracks by a Mexican teachers’ union has ended after 91 days, Mexico Daily News reports. National Guard troops cleared the tracks in the state of Michoacán on Sunday afternoon, and KCSM trains were expected to begin running the same day. An industry association […]
Read More…










