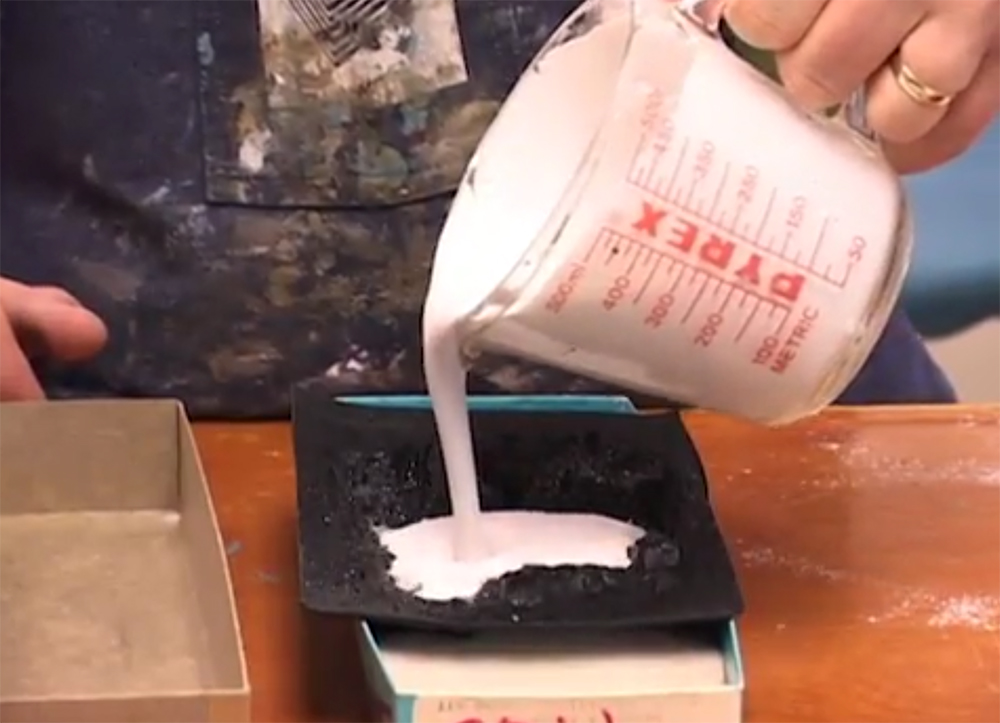

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Hydrocal is a useful material for modeling scenery on a model train layout. Follow along and learn how to pour Hydrocal into rock molds to make cliffs and rockfaces for model railroad scenery. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Hydrocal is a useful material for modeling scenery on a model train layout. Follow along and learn how to pour Hydrocal into rock molds to make cliffs and rockfaces for model railroad scenery. […]
Read More…
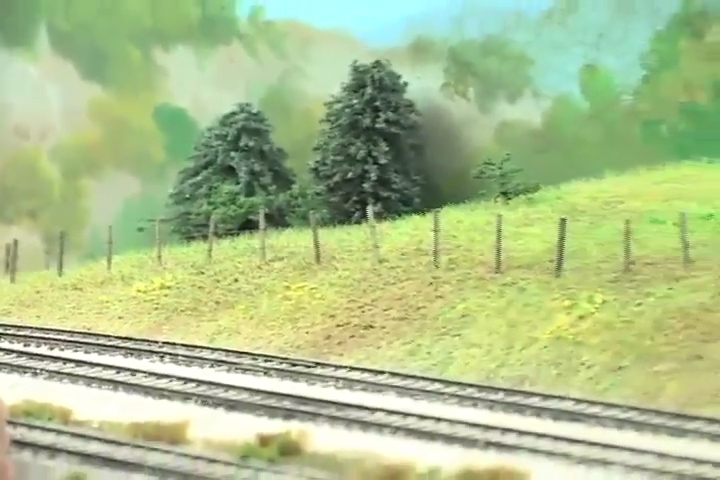

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Model Railroader associate editor Cody Grivno shows how to model a wire fence. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Model Railroader associate editor Cody Grivno shows how to model a wire fence. […]
Read More…
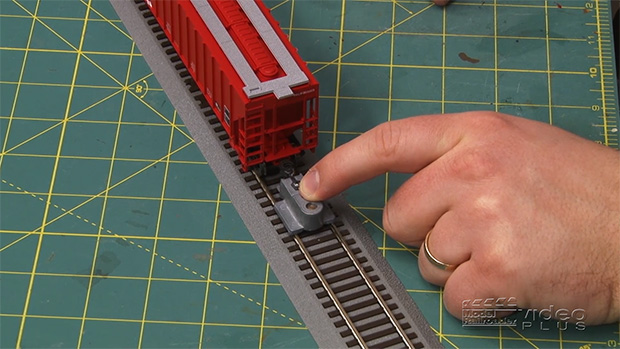
Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Couplers are what hold the cars together on a model railroad. They can also cause problems if they are not set properly. Cody Grivno shows you how to check to make sure your couplers are in good working order, and what to do […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Couplers are what hold the cars together on a model railroad. They can also cause problems if they are not set properly. Cody Grivno shows you how to check to make sure your couplers are in good working order, and what to do […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Model Railroader associate editor Cody Grivno shows you how to add ground cover and other easy scenery techniques to your model train layout. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Model Railroader associate editor Cody Grivno shows you how to add ground cover and other easy scenery techniques to your model train layout. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Many of today’s limited run models are made using resin. Although similar to plastic, resin requires different adhesives to assemble the parts. This video shows how to do the job using cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page Many of today’s limited run models are made using resin. Although similar to plastic, resin requires different adhesives to assemble the parts. This video shows how to do the job using cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue. […]
Read More…

Having trouble viewing this video? Please visit our Video FAQ page There are many different paints available for modeling work, and in this video Cody Grivno explains the basics and uses of several common brands. […]
Read More…

Basic Training is a series of videos for modelers just starting out in the hobbby. In this episode, learn how to properly use rail joiners to connect sections of track for your model railroad. […]
Read More…







